May Co. division based in Houston. Continue reading
I remember getting two phone calls from Beverly Ingraham1, the Advertising Director at the May Company division based in Houston, Foley’s. The first one came in early 1993 before we had hired Doug Pease to handle our marketing. I spoke with Beverly about AdDept, TSI’s administrative system for large retail advertisers. She had learned of it from one of our mailings.
I informed her that we had installed the system at a “sister division”, Hecht’s. I emphasized that it had been helping the employees at Hecht’s with their monthly May Company reports as well as many quotidian administrative tasks. She asked me to fly to Houston and show the system to them. Although I don’t remember the occasion, I must have spent a day or two talking with potential users, primarily Richard Roark2 in the business office at Foley’s off in one of the top floors of the flagship store on Main Street. The demo must have been at an IBM office. Sue might have come with me to Houston, but neither of us remembers the trip. We met Beverly and Linda Knight, the Senior VP of Advertising3. The people at Foley’s all seemed enthusiastic and exceptionally nice, as they did every time that I visited there.
After we returned to Connecticut, I wrote up a proposal to run the AdDept system on the F10 model that had recently been introduced by IBM. There is little doubt that I also included quotes for some custom programming—I forget the details.
I was very excited about this. I knew that Foley’s advertising must have had money because the May Company had recently merged the D&F division, which had been based in Denver, with Foley’s. The combined operation would be run from Houston. That gave them stores in Arkansas, Louisiana, Texas, Oklahoma, New Mexico, Arizona, and Colorado. The May Co.’s purse strings were bound to be a little looser than usual.
I was also excited because I was quite certain that most of the work that we had done for Hecht’s would be usable for Foley’s with only minor adjustments. For once we seemed to be on familiar ground.
Over the next week or two I talked with Richard Roark about some of the items in the proposal. When I finally got the second call from Beverly, she did not immediately say that the project had been approved. I had to ask her. She said, “Oh, yeah. Sure.” She then corrected my assumption that Richard Roark would be the liaison. She assured me that she would tell me who it was, and she did a little later.
I remember very well my first visit to Foley’s in May of 1993 to install the system. I flew on Continental Airlines from Bradley to Intercontinental Airport4, which was twenty-three miles north of the city center. I took a shuttle bus to the Hyatt Regency Hotel, which was only a couple of blocks from Foley’s headquarters.
The Hyatt featured a lobby that was both luxurious and sometimes very noisy. A bar was right in the middle of it, and the area above was open all the way up to the roof, thirty stories up. It was like an echo chamber or a natural amplifier. So, half of the rooms had windows that viewed the lobby. After my first stay there I always requested a room with an outside window.
The elevators all had glass walls on the lobby side. I am not ordinarily affected by heights or tight locations, but the rapid descent in these glass cages made me quite uneasy.
I distinctly remember my first stroll to Foley’s from the Hyatt. It was March. I knew that I would not need the overcoat that I had worn to the airport in Connecticut, but I did have on a wool suit. The lobby of the Hyatt was very cool. I went through the revolving door and I was smashed in the face by the heat and humidity. It was like walking into a sauna.
By the time that I swam walked the few blocks to Foley’s big brick building, I had grown tolerant of the humidity. However, I was not expecting to see ten or so mendicants sitting on the sidewalk near the employees’ entrance. This crew was not the aggressive kind I had encountered in my life in Detroit and visits to New York. They just seemed hopeless. I don’t know why, but I was shocked to see this in Texas.
I don’t actually remember too much else about that day. That is a good thing. In TSI’s thirty-five year history we only had a few near-disasters or crises, and I distinctly remember each one.
I recall that one of our first big assignments for Foley’s was when the Houston Chronicle bought out the Houston Post and its assets in 1995. Foley’s was by far the largest advertiser in both papers. They ran dozens of ads every week, and the newspaper coordinators had already recorded the schedules for both papers for several months ahead.
Their first requirement was a list of all ads that were scheduled to run in the Post but not the Chronicle. That was not difficult; I wrote a query to produce the list. They would need to decide what to do with those ads and adjust the schedules for the Chronicle where necessary.
Next, they needed to delete all of the ads scheduled for the Post. This was was a little more difficult. I had to replicate exactly the process that would have occurred if they canceled them individually. That meant that I had to write history records for each deletion, and all subsidiary files and summary records needed to be updated as if the deletions were being done one at a time.
Finally, they needed me to find all the ads in the Chronicle that were full depth (the longer dimension), which, if memory serves, was twenty-one inches. All of these ads would be one-half inch deeper because the Post’s presses, which the Chronicle planned to use going forward, cut the paper to that size. That meant that the costs (Foley’s kept track of actual costs billed by the papers and costs marked up to reflect production expenses that they showed the merchants) had to be recalculated.
Since any paper could change its size (and many subsequently did), I made this one into a program that could be attached to a menu available to the users. Since AdDept’s rate calculations had been externalized into separate callable modules, this was also not too difficult. History records and updates of subsidiary files and summaries were required for this step, too.
They needed all of this in just a couple of days. There was no test environment. No one helped me, and no one tested the code that I produced. On TSI’s developmental system I simulated a few ads of each type and tested the code on them. When I felt satisfied with it, I sent the code to Foley’s over the phone lines, crossed my fingers, and ran the programs.
I must have done a pretty good job. No one complained.
Visits to Foley’s were frequent during the nineties. Sometimes they wanted training, but usually they wanted to describe enhancements that they desired. Two of the trips had a comical aspect. The first one was when I asked Sue to take one of the early trips for me. I cannot remember what the objective for the trip was. She did not have a credit card in those days, and she forgot to bring any cash. Fortunately, someone at Foley’s cashed a check for her, or she might have needed to join the beggars clustered by the employees’ entrance.
On another occasion I wore my running shoes on the flight to Houston. When I had arrived in Houston, as usual I took the shuttle to the Hyatt. When I opened my suitcase at the Hyatt, I was aghast to discover that I had brought only one leather shoe. How could my valet have been so careless?
I recalled that I had seen a Payless Shoe Source, at one time a division of the May Company, between the hotel and Foley’s. I bought a pair of black leather shoes at Payless for $20. They were so uncomfortable that I threw them away as soon as I arrived home after the trip. However, they saved me from embarrassment during the three days of that visit. I figured that my misbegotten purchase was the equivalent of a bargain-priced rental for less than $7 per day.
Our first liaison at Foley’s was Robert Myers5. I think that he must have come from the IT department. He helped to set up a system whereby the store managers could view the contents of their ads on systems in their stores before the ads were run. He tried to get me (of all people) to market the arrangement to other retailers. I suppose that he meant that we should try to offer it as an enhancement to AdDept, but the guts of what he had done involved infrastructure that was unique to Foley’s. I didn’t understand most of it, and I was too busy with things that I understood a lot better to devote time to learning it.
Robert attended nearly all of the training sessions when I came to Houston, and he did a good job of writing up software requests when I was not around. He was one of our best liaisons.
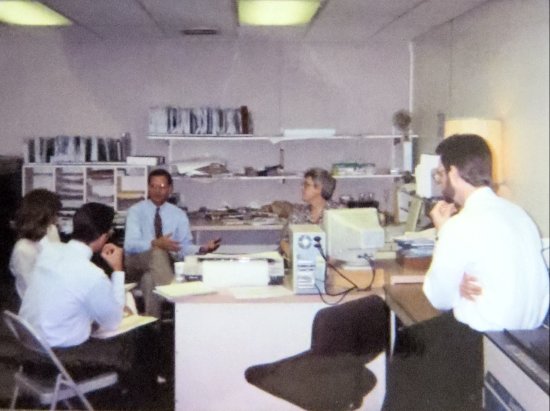

Robert once expressed the opinion to me that XML would become the solution to all of the interoperability problems of software systems. I had read a little about it, but I did not understand it. He did not do a good job of explaining it. He may have been right, but to my knowledge XML never entered the main stream among software developers. TSI implemented a lot of interfaces with software from other companies. Sometimes we sent them files, and sometimes AdDept received and processed files. We never considered using XML.
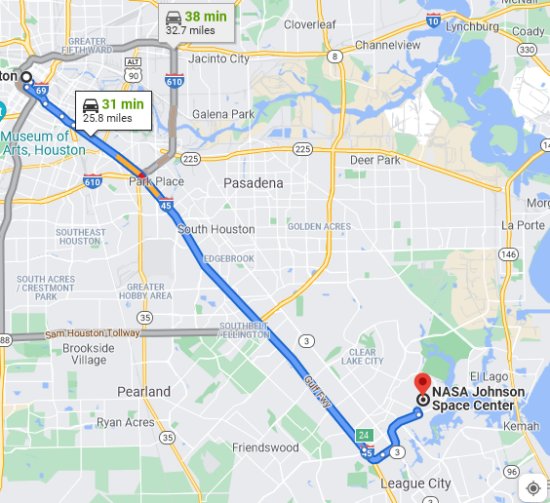
One day Robert took me on a road trip. This must have been over a weekend, probably the one in which I oversaw the migration from the F10 that Foley’s initially purchased in 1993 to a faster model with more capacity, the 270.
We drove down7 to the Johnson Space Center (now called Space Center Houston). We spent some time at the exhibits that they have about manned space flight. It was OK, but ever since I was required in 1967 as a member of the varsity debate team at the University of Michigan (explained here) to argue against the concept of putting an American on the moon, it has always seemed to me that it was an expensive and dangerous idea with very little payoff. So, I was not as gung-ho as most of the visitors to the center.
I found notes that indicated that I went out to dinner with Robert Myers and his wife in 2000. I have no clear recollection of the occasion.
The May Company determined that AdDept should be installed in all of its department store divisions. The process of reaching this decision is described here. Robert was assigned by the May Company to help with the installations at several other divisions. On a few occasions we crossed paths at other divisions.

Beverly Ingraham had a nameplate on her desk that said “Bevo”. I don’t know whether she was an alumna of UT8, or if it was a play on her name. Maybe both.
I remember doing one project that Beverly was especially interested in. The IT department was able to provide us with sales by department by store by day. I wrote a program to convert this file into a usable format for AdDept programs. We then used the information in reports and screens for each merchant that showed them in each market the total costs of their ads (or parts of ads) and the associated sales.
The ability to provide this kind of information was a big feather in Beverly’s cap. This was the first of several TSI projects aimed at evaluating the productivity of the advertising. The concept was actually more useful as a sales tool to show the power and reach of the AdDept system than as a practical tool for the advertisers. If more than one media was employed for a sales event, it was impossible to attribute which of the ads produced the results.
I don’t have distinct memories of most of the projects that we undertook for Foley’s. For the ones after Denise Bessette became VP of Software Development (as explained here) I only wrote up the requests. I don’t have an excuse for forgetting the ones between 1993 and 1997 I probably did most of the coding myself.
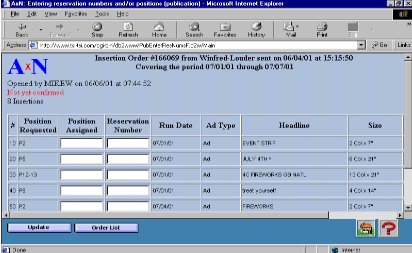
I unearthed some notes for a visit in 2000 about insertion orders for newspapers. Foley’s two newspaper coordinators were Hedy Wolpa9 and a lady named Leila, whose last name I don’t remember. I was shocked when they told me that they had not been faxing insertion orders to the papers directly from the AS/400 because they could only order by date, not by publication. They thought that this made it difficult for them to specify positioning (such as “Back page of main section”) while ordering. I also learned that they also did not realize that they could specify much longer special instructions as well.
This would never do. They had paid us to provide insertion orders in the precise format that Foley’s had specified, and they had paid IBM for the faxing hardware and software. We might have even gotten a commission on that. Furthermore, TSI needed for them to be ordering in AdDept so that we could switch them to using the product that we were about to release, AxN (described here).

While I was at Foley’s I wrote a new front end program for the insertion orders. It allowed them to order for one paper at a time. They were very happy; it was just what they wanted.
Denise hated for me to do things like this on the road. She did not want me to modify any code on the fly. I understood that. In this case, however, I thought that it was better to beg forgiveness rather that to ask permission from Denise. The top priority of this trip was to get Foley’s on board for insertion orders. They became an enthusiastic users, and all their papers subscribed to AxN10 a soon as we made it available.
Foley’s was, by most measures, our best client. They used almost every aspect of the system. They even used the SmartPlus interface for broadcast that was originally designed for the GrandAd system for ad agencies. Their agency, which was in Dallas, sent them files with schedules and audit data.
Several Foley’s users also became very adept at using Query/400 to design some of their own reports. They used this product as much as or more than any other client. They sometimes used their queries and a product called ShowCase Strategy without any assistance from TSI.
As of 2000 TSI had delivered and installed approximately 200 custom programming projects to Foley’s.
1. Beverly Ingraham was promoted to Senior Vice President of Advertising at Foley’s in January of 2000. She held that position until the division was dissolved after Macy’s acquired the May Company in 2006. I am pretty sure that she went to the Macy’s Central division in Atlanta and headed the advertising department there for several years. I think that in 2021 she lives in Spring, TX, twelve miles north of the airport. If I am correct, then she is my age and therefore probably retired.
2. Richard Roark’s LinkedIn page is posted here.
3. In 2000 Linda, who was by then known as Linda Knight Quick, resigned as Senior VP of Foley’s to take a job at Penney’s. Foley’s sued to prevent this because of a non-compete clause in her contract. I was unable to determine how the situation was resolved.
4. In 1997 it was renamed George Bush Intercontinental Airport.
5. I have a note from January of 2000 that indicated that he was doing Internet development for Foley’s IT department using Cold Fusion, but I do not know what he has been up to in the last two decades.He helped me identify some of the people in photos of employees from Foley’s and other May Co. divisions. He also said that his association with TSI changed his life, but he did not explain how.
6. Doug Pease was TSI’s most successful marketing director. Much more can be read about him here. I think that Doug and I must have stopped at Foley’s as part of a marketing trip to Stage Stores, also in Houston. That installation is described here.
7. I wonder if I had a rental car for that trip. Robert lived a long way from downtown Houston. He generally took the bus to work!
8 The mascot of the University of Texas Longhorns is a steer named Bevo. The current one in 2021 is Bevo XV.
9. Hedy Wolpa’s LinkedIn page can be viewed here. She worked at Foley’s for thirty-one years!
10. The design of AxN is described in some detail here.


















 Needless to say we are concerned about what effect the realignment will have on TSI. We have spent the last 17 years developing AdDept, the software product which has become the standard of the industry for administration of retail advertising departments. The May Company was our largest client.
Needless to say we are concerned about what effect the realignment will have on TSI. We have spent the last 17 years developing AdDept, the software product which has become the standard of the industry for administration of retail advertising departments. The May Company was our largest client. Since that time, as I wrote you earlier, most of the rest of the department stores in the country—as well as several other large retailers like Dick’s Sporting Goods—have successfully implemented AdDept in their sales promotion departments. They were able to get affordable systems tailored to their requirements. AdDept is not a sexy system, but it gets the job done.
Since that time, as I wrote you earlier, most of the rest of the department stores in the country—as well as several other large retailers like Dick’s Sporting Goods—have successfully implemented AdDept in their sales promotion departments. They were able to get affordable systems tailored to their requirements. AdDept is not a sexy system, but it gets the job done.