A true multi-user system. Continue reading
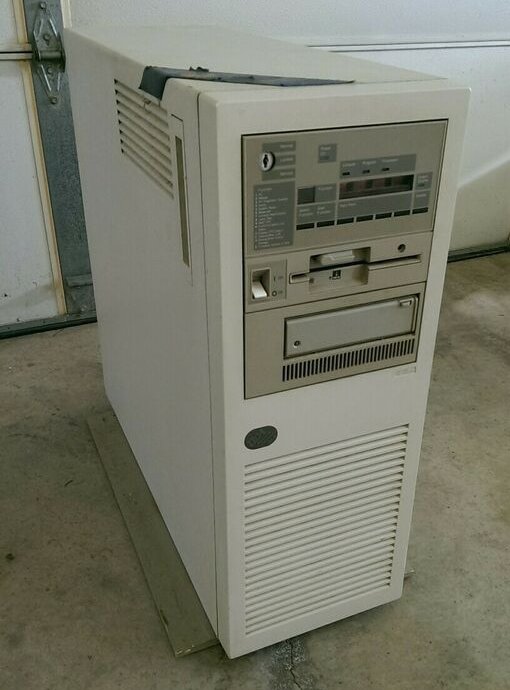
IBM’s introduction of the System/36 (S/36) in May of 1983 was not a monumental event for TSI. From our perspective the new system seemed more like a marginal upgrade of the System/34, which had always been much too pricey for anyone who would talk to us. The new system had only one basic model, the 5360. The starting price for one of these was still $140,000. It was also gigantic and had special electrical requirements. It was clearly designed for a small data processing department, not a small business without one.
The biggest advantage of the System/36 over any system that we had worked with was that it supported a fairly large number of terminals and printers. This was because it could run a number of jobs at the same time. It also supported batch processing, which meant that time-consuming jobs need not tie up any workstations.
We appreciated these benefits. In fact, we drooled over them. However, no prospective customer of ours ever had a six-figure budget for hardware.
The peripherals were also rather expensive. IBM in those days ignored standards used in the rest of the industry. It set its own standards, and they were all proprietary. So, cheaper hardware from other vendors would not work with IBM systems.
Although the price went down through the years, a 5250 terminal cost around $2,000 when the 5360 was introduced. The cheapest printers, which used dot-matrix technology, were in the $5,000 range.
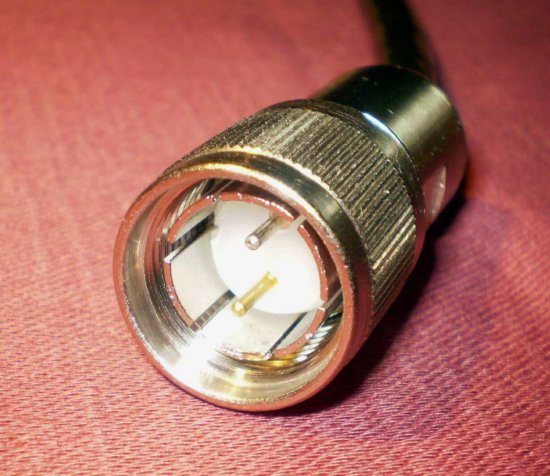

The cabling was also not cheap. The system used twinaxial cables for direct attachment of these devices. Most competing systems used serial or parallel connections. Twinax was decidedly better, but it was also more expensive.
The local devices were connected in a serial fashion to a controller. Up to seven devices could be connected on one twinax line. Each device had two female twinax connections on the back, either in one T-shaped unit or with two short cables. One was called the “gozinda”; the other was the “gozouta”.
So, if the S/36 had four devices named A, B, C, and D. A would be connected to the controller by a twinax cable, B would be attached to A by a twinax cable, C would be attached to B, and D would be attached to C.
A switch on device A, B, and C needed to be set to allow pass-through to the next device on the line. On device D that switch needed to be set to denote that it was the last device on the line.
For device D to communicate with the S/36, all of the connections must be functional, and all of the switches set correctly. It reminded me of Christmas tree lights in the old days.
The S/36 also came with a serial port. Since a modem could be attached to this device, it would be possible for support people at IBM or the software vendor (or anyone else, for that matter) to sign on from a remote location. This was, of course, our dream; it would make support so much easier. The announcement brought it a little closer to reality.
The hard drive capacity varied from 30 MB to 400 MB. In the twenty-first century, of course, those quantities would only hold a handful of photos. However, to most software vendors in the eighties this meant that total storage was no longer a big concern. However, the default backup device was a magazine that held only ten 8″ diskettes. Each diskette had a capacity of only 1MB each. This was a rather obvious limitation on the practical storage.
It was possible to attach an 8809 1/2″ reel-to-reel tape unit to address this. I could not find a price for these monsters. It may well have been the case that if you had to ask the price, you could not afford it.
The System/36 had two processors. The main processor (MSP) executed the code; the control processor (CSP) managed the work for the main processor. The CSP was four times as fast as the MSP, and they worked perfectly in tandem. The S/36 could perform an amazing amount of work at very fast speeds with embarrassingly puny processors. It was also extremely reliable.
Some actions, such as IPL1 and backing up files, needed to be initiated from the system console. The system console on the 5360 was built in to the top of the box. Your system operator needed a wheelchair? Life was rough all over.
The System/36 supported five programming languages: RPG II2, COBOL, FORTRAN, BASIC, and Assembler. RPG II, a simplistic column-based language, was the most popular. Wikipedia says that this was because it was the least expensive3. The BASIC language was similar to the one used on the Datamaster. I never heard of anyone who programmed in FORTRAN or Assembler on a S/36.
BASIC programs could not be compiled. Therefore, a copy of the BASIC interpreter needed to be loaded into memory for each program that was running. Nevertheless, because the CSP was so efficient, TSI’s benchmarks showed that there was no noticeable difference in the speed of interpreted BASIC programs and compiled RPG II programs performing the same tasks. So, we never considered converting our program to anything besides S/36 BASIC.
IBM also positioned the System/36 with its DisplayWrite/36 software as a word processing server. We found it to be inferior to the Datamaster product in most ways.
The file structure of the S/36 was somewhat different from the Datamaster’s. Programs and other executable items such as BASIC procedures and system procedures were stored in “libraries”. Libraries were somewhat like directories or folders on a PC. However, there was no such thing as a sub-library.
Data files needed to have unique names. They did not reside in libraries. In order to identify which files belonged to which application, the names were preceded by a short identifier and a period. In GrandAd all the media files started with “M.”, and the other files started with “T.”.
The S/36 did not have a relational database4. However, the fields in each file were defined in the system using field names, positions, and length/type designations. These data definition specifications were called DDS. Programs could access files using the same ISAM techniques with which we were already familiar. However, IBM also offered a product named Query/36 that allowed someone who know how the files were named and structured to write queries in a manner that was similar to SQL. These queries could then be saved and executed on demand.
Query/36 was a valuable debugging tool. TSI required all of our clients to buy it.
IBM announced the 5362 in 1984. It was much smaller than the 5360—only about as large as a two-drawer file cabinets. It also had no special electricity requirements. It used the same operating system as the 5360, which was called SSP. It came with one diskette drive and up to 120MB of hard drives. A QIC (1/4″ cartridge) external tape drive was available. A 5250-type terminal plugged into the first twinax spot served as the system console. Fewer devices could be attached, but none of our clients ever reached the limit. Best of all, the starting price was only $20,000, about the same as two Datamasters and a hard drive.
Many advertising agencies in the northeast could afford this level of investment. It took some time for TSI to convert the ad agency programs. I remember spending many days at IBM’s office in Hartford working on this. After tat we needed to change the focus of our marketing efforts to larger ad agencies. At this point IBM had no system to offer to the many whose needs would be satisfied with one Datamaster with diskette drives.
We were happy with this announcement, but it was a disappointment that IBM had totally abandoned the market that had produced the majority of TSI’s sales.
The 5364 (or System/36 PC), which was announced in June of 1985, was IBM’s belated attempt to recapture that market. The starting price of $5,995 was quite attractive. For some reason the system console had to be an IBM PC, XT, or AT with a special card inside. The S/36 part was the same size and shape as an AT. It contained a 5 1/4″ diskette drive that was compatible with neither the attached PC nor any previous model of the S/36. Compatibility was not a high priority for IBM.

This bizarre arrangement was very difficult to explain to a prospect. Why would a super-reliable S/36 be coupled to the least reliable hardware ever to wear the IBM logo? It did guarantee that at least one IBM PC was installed at each location, I guess. However, most installations probably did what we did—attach the oldest, slowest machine available as the system console, and then use it only when necessary.
The 5364 had two severe limitations. In the first place, only four devices (counting the system console and the printer) could be attached. So, the S/36 customer could really only attach two more displays or one display and a printer. Still, that would suffice at most small ad agencies and at TSI. We immediately ordered one.
The other limitation was, in some ways, worse. The 5364 came with only 256K of RAM. Each session could use up to 64K. However, batch jobs counted as sessions. If one person started some lengthy reports or other process, the system could possibly reach the point where jobs needed to be swapped between memory and disk. This could severely impair the system’s performance.
The announcement of the 5364 created a good deal of business for a company named Black Box. They sold a box with slots for one 8″ and one 5 1/4″ diskette and software to make image copies from one to another. We bought one, and I used it a lot.
In 1987 IBM finally fixed all of the problems, at least the ones that most concerned us. The 5363 was a reasonably priced machine that was suitable for almost any small business. If it had been announced two years earlier instead of the 5364, we could have sold a lot of them.
I could not find anything either on the Internet or in our basement that listed the price of one. I don’t remember that anyone balked at the cost. I also could not discover how much memory it had, but I remember distinctly that it was plenty. It could handle at least seven devices, too, and you could get one with a built-in QIC tape drive.
We enthusiastically ordered one for TSI’s office and tried to get our Datamaster customers excited about it.
By the middle of the eighties most office workers had some kind of personal computer on their desks. They did not want someone to install a terminal next to it as well. But how could they gain access to the S/36 without a terminal? There were no networks worth mentioning in the eighties, and there was nothing like USB. The only way to reach the server was through a twinax line, and IBM did not share its knowledge of how the display and printer connections worked. IBM considered anything that it produced was proprietary.
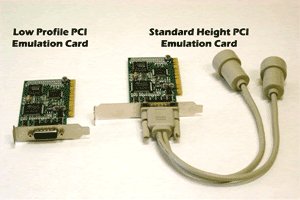
IBM and many third party companies brought 5250 terminal-emulation packages to market. The idea was to be able transform the PC into a terminal on demand and then change it back. Although the other vendors had to reverse-engineer the 5250 interface, they still were able to produce competitive products that were cheaper and had more features than what IBM offered. They generally consisted of a three pieces:
- A hardware card that fit into an expansion slot on the motherboard of the PC. That’s right. You had to take the cover off of the machine and add a card that had the brains needed to make the PC act like a 5250 card. You might also need to physically flip switches on the care to configure it. Then you had put the PC back together again. What could possibly go wrong?
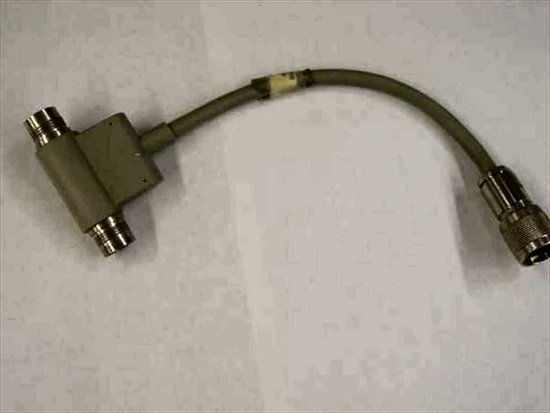
- A dongle (sometimes lovingly referred to as a “pigtail”) that screwed into the interface on the part of the card that stuck out the back of the PC. It provided a gozinda and a gozouta for the twinax cable(s).
- Software to run on the PC.
When they first appeared, the cost of these packages was well over $1,000, nearly as much or more than a PC or terminal. However, the emulators had one very substantial advantage. The inexpensive printer attached to the PC could also be configured as a S/36 printer. This not only saved money and office space; it was also much more convenient.
For a few years the companies selling these packages did a land-office business.
1. IPL stands for Initial Program Load. It just means the starting process for the system. IBM had three-letter abbreviations of everything, including a three-letter abbreviations (TLA).
2. RPG is short for Report Program Generator. I could never understand why anyone used it.
3. IBM required separate licenses for each programming language that was used.
4. Two IBMers, Donald D. Chamberlin and Raymond F. Boyce, codified the Structured Query Language (SQL) used in relational databases in the seventies. IBM rejected it because the Indexed-Sequential ISAM structure that it used in its computers had much better performance. About three decades later the company changed its mind.








Pingback: 1985-1988 TSI: GrandAd: The System/36 Conversion | Wavablog
Pingback: 1988-2014 TSI: The Programmers | Wavablog