Supporters and coders. Continue reading
TSI’s first, last, and best programmer was Denise Bessette. For three decades she was one of the most important people in my life. More details about her relationships with TSI, me, and the rest of the crew can be found here.
During the years that Denise worked only part-time most of the programming burden fell on my extremely narrow shoulders. By 1987 it had become too much. We needed to hire a full-time programmer. I placed ads in the Hartford Courant and the Journal-Inquirer. It was not a good time to be hiring. The state’s unemployment rate was heading toward a record low of 2.8 percent, and the demand for programmers far exceeded the supply. I understood that a small firm like TSI would be at a disadvantage when competing with giants like the insurance companies. Besides, our office was in a converted barn, and we were not able to offer any benefits to speak of.
A few people responded to our ad. The only one that I had any interest in hiring was Sandy Sant’Angelo, whose name was Sandy Scarfe when she started at TSI. She had taken a few programming classes. She worked for the Springfield (MA) Public Library system. A major part of her job there was helping to set up the new computerized system for keeping track of the books. This was not very close to anything that we did, but at this point my choices were to hire her or start the recruiting process over. I chose the former.
Sandy turned out not to be a great coder, but she had other traits that I valued highly. She learned how to use the computer systems rather quickly, and if a project was well-defined, and I provided her with a somewhat similar program to use as a model, she was eventually able to save me a little time. What I liked the most about her were her dependability and her attitude.
Unfortunately, the great bulk of our work in the nineties was quite complicated, and it became more and more difficult for me to find appropriate projects for her. One thing that I had noticed was that she was good at talking to the users at our clients’ installations. She had a cheerful demeanor, and she was pretty good at getting to the bottom of problems.
At the time TSI’s office had two telephone lines1, a generic number that we published in our promotional materials and a support line that we provided to our clients. I decided that Sandy’s primary responsibility should be answering calls on the support line. If they were simple questions, she could deal with them immediately. Otherwise, she recorded them. At first we kept track of the problems on paper, but soon we devised a simple system for recording them in a database available to all the programmers.

This system worked pretty well. The key question that we asked was whether the problem was holding up the client’s work. If it was, the problem was automatically escalated. In nearly all cases these problems were addressed the same day.
I did not often work closely with Sandy. Actually, no one did. Her telephone voice sounded fine on the other end, but for some reason it really carried inside the office. I had to move her desk away from the programmers’ area.
Although I had hired Sandy, when Denise took over application development, she became the boss of all of the programmers. After a few years, Denise, who knew Sandy’s limitations, decided to eliminate her position. The meeting in which she was the terminated was very hard for me to witness. Sandy broke down and cried. I understood that Denise had made a business decision, but I doubt that I could have done it. By then I thought of Sandy as part of the TSI family. Nevertheless, I never considered overruling Denise’s decision.
I don’t have a lot of vivid memories of Sandy. She got married after she came to work with us, and she seemed happy. Her attendance record over the years was nearly spotless. She also attended all of TSI’s summer outings and Christmas parties.
I only recall her expressing a strong opinion about one thing. She loved the Harry Potter books. Her endorsement, however, was not sufficient to prompt me to dip my literary beak there.
Sandy was the person who alerted the rest of the office about the attacks on 9/11/2001. Everyone else in the office was shocked at this, but I had spent more time in airports than the rest of them put together. The airport security by that time was unbelievably lax. I had concocted in my mind at least three ways of sneaking a gun aboard a plane. It was also no surprise to me that plenty of people in the world who despised the United States for its arrogant and interventionist foreign policy and its unquestioning endorsement of anything done or said by Israel.
I find it personally embarrassing that I know so little about Sandy, a person with whom I worked for more than a decade. I just let her live her life as she wanted to and expected her to come in every morning. I can never remember her asking for anything.
After assigning Sandy to answering support calls, I reckoned that we needed another programmer. The Internet was still in its infancy, and so the process again involved expensive want ads in the local papers. Before finding someone who fit the bill I hired two different people, neither of whose names I remember.
The first was a woman in her twenties or maybe early thirties who already had programmed in BASIC at another company. I hired her. I was pretty excited about the prospect of working with her. It seemed likely that she might be able to get up to speed in record time. On the first day she appeared in the office at 8:30, TSI’s starting time. I immediately put everything aside to help her understand how we programmed and to go over some of the peculiarities of the hardware and operating systems.
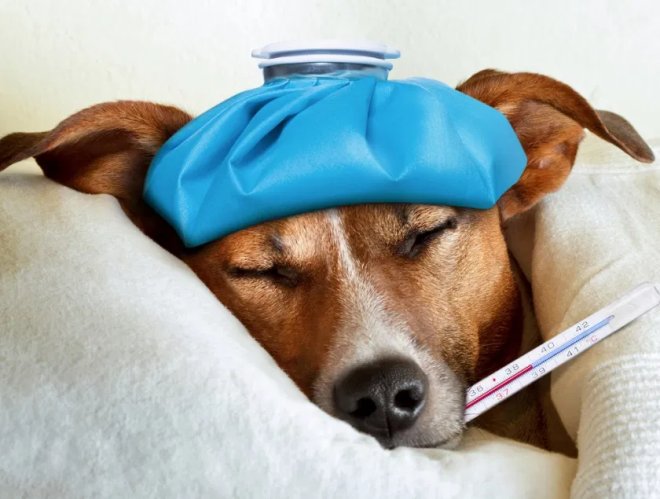

At some point she must have received a phone call. It only lasted a couple of minutes; I thought nothing of it. However, just before lunch she told me, “I’m sorry, but this won’t work. My dog is sick, and I need to be with him.” I don’t remember what I replied, maybe nothing.
I immediately initiated another job search. This time I hired a guy in his twenties who claimed to have done some programming for a previous employer. I spent a couple of weeks training him, and he seemed to be making little or no progress. I began to doubt that he had ever written a program, or at least one that did approximately what was required.
I have only a vague recollection of what he looked like or anything about his personality. I do remember that he was into the martial arts and worked out. He was in very good shape.
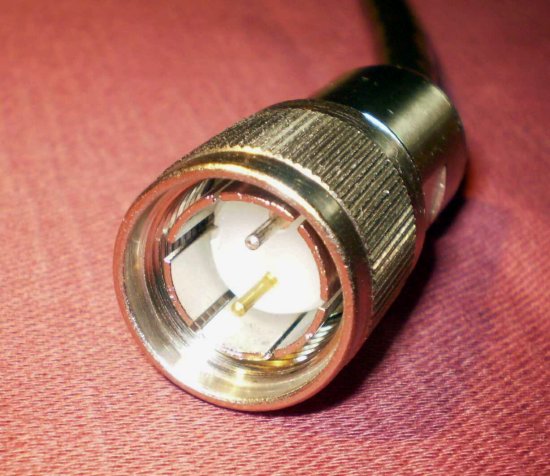
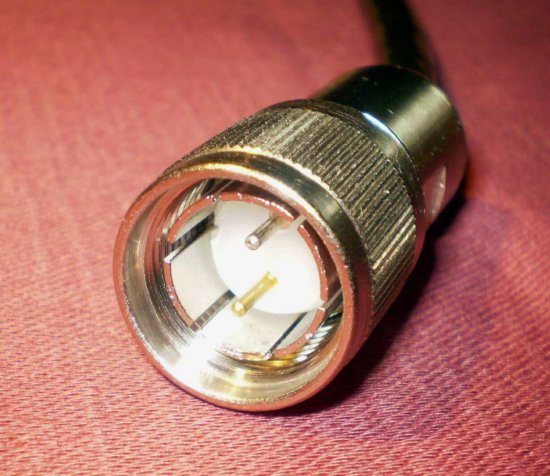
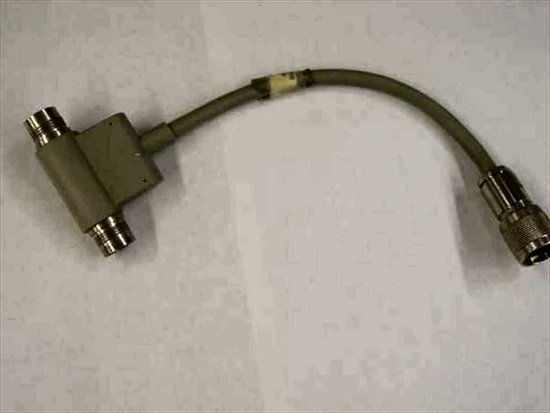
I probably would have worked with him for another week or two before deciding, but we had a twinax connectivity problem. As is explained here, the individual terminals and PC’s were connected to the server via twinax cabling. Each station was dependent upon the cabling, pigtails, and settings of the other devices on the line. Some of our cables were very long. We ordered these custom-made from a company in New Britain. They were expensive. Moreover, the company needed a little time to make them, and it was located forty or so miles from TSI’s office.
It was an “all hands on deck” situation until we got the situation resolved. Everyone was checking connections. I asked the new programmer to connect one of the cables to one of the devices. I showed him how their were two holes on the “pigtail” and two pins on the end of the cable. The pins, of course, fitted into the holes. Once the connection was made, a cap on the end of the cable could be turned so that it was impossible for the cable to come loose. I honestly thought that it was impossible for anything to go wrong. I had done this many times, and nothing had ever gone amiss.
We spent an hour or so trying to get the line to work, but we had no success. I eventually examined the connection that this new fellow had made. The pigtail was tightly attached to the cable. I unfastened it and looked inside the head of the cable. Both pins were bent at a 90° angle, one to the right and one to the left. They resembled a pair of arms stubbornly crossed on someone’s chest. I would have bet that no one was strong enough to do this. To this day I had no idea how he accomplished this feat.
I was so angry that I had to retreat into Denise’s office for a few minutes so that no one could see me. I decided on the spot to fire him, but I waited until the end of the day to do it.
I thought at first that we would need to order another custom cable. However, we found a spare cable, and with a few adjustments to our wiring scheme, we were able to get the connectivity resumed within a half hour.
Twice when I advertised for a programmer, I received applications that I could not believe. One was from the lady who was IT director at Casual Corner3, a large retail chain. Their home office was in Enfield. My customary jogging route took me right past their complex. The IT department even had an AS/400! Casual Corner did not advertise much, but with and “in” we might even get an AdDept installation out of it. I tried to contact her, but she never scheduled an interview.
The other guy was retired. He had been an IT director at a large company. He came in and talked with me. He said that he would work cheap. He just wanted to write code. I don’t know whether he would have been a good programmer or not, but my primary interest was elsewhere. At the time we were just beginning to try to work with IT departments, and the process always left me frustrated. I thought that having this guy on TSI’s team might help me learn how managers of IT departments made decisions.
It was a close call, but I decided not to make him an offer.
Instead I hired a much younger guy, Steve Shaw. He had been an RPG programmer at Riverside Park4 in Agawam, MA. He picked up BASIC pretty quickly, and I was able to give him reasonably challenging projects. I really liked working with him. When he started his coding was a little sloppy, but the quality improved quickly. When I told him this, he seemed slightly insulted.
While he was working at TSI Steve acquired a multi-unit property in Massachusetts. I could not understand why he wanted to be a part-time landlord. To each his own.
Steve was something of a daredevil. He purchased a jet ski while he worked for us. At some point he disclosed that he had been in a motor cycle accident in which he lost a number of teeth. I wrote a little song to cheer him up. My sister Jamie and I performed it for him in the office. It was a smash hit.
I found a copy of the lyrics:
On corn cobs I’d be gnawin’.
I could graze upon your law-n.
It is my firm belief.
My dentitions would be so neat.
I’d devour piles of roast beef,
If I only had some teeth.Oh, I could eat a pie.
I’d chew up all the steaks that you could buy.
I’d masticate on pork chops bye the bye.
If you object,
I’ll bite your thigh.From ear to ear I’d be grinnin’.
Music by Harold Arlen; Words by Mike Wavada
Young girls’ hearts I’d be winnin’.
I’d steal them like a thief.
I would floss away my tartar,
and stop actin’ like a martyr,
If I only had some teeth.

Steve only worked with us for about four years. I appreciated that he might see it as a dead-end job. However, the work was, I think, potentially very exciting. We were solving problems that no one had addressed before for large corporations that everyone has heard of. I tried to talk him into staying, but there was no way for me to argue that he could ever climb the corporate ladder at TSI. We did not have a ladder.
The next programming hire was Harry Burt2, who was almost exactly my age, forty-something. He had a degree in math, and he had programmed in BASIC. He had been a vice president at a bank in Simsbury (I think) that had had closed under fairly suspicious circumstances that did not involve Harry. I hired him and terminated the job search at the end of my interview with him.
Harry mostly did programming projects for us. However, I also assigned him to monitor the work of Fred Pease in the huge Y2K project, which is described here. Fred was a college student who had never had a job before. The plan was for him to work part-time at TSI for the summer. He wanted to set his own schedule. By his own omission he tended to stay up late playing video games. Sometimes he stayed up all night.
That much was OK, but Fred constantly changed his schedule without telling Harry or anyone else. Harry had to ask him every morning how long he was going to work. He usually said “Until 11:30” or “Until 12:30”. The last straw was when he said “Until something-thirty”.
Fred’s work was also slipshod. I decided that I needed to take the project more seriously. If I was going to need to check every program anyway, I decided to do it all myself. Frankly, I did not want to assign such a tedious and unrewarding task to any of my good programmers. I did not want risk losing them. I took it on as a sort of penance; I should have seen it coming back in the eighties.

Harry (who was NOT hairy—I thought of the Fuzzy Wuzzy rhyme whenever I saw or heard his name) was a great fit for TSI for at least a decade. After a couple of years I began to worry that Harry might realize that there was no path for advancement at TSI and decide to look for work elsewhere. After all, he was definitely overqualified for his job.
I decided to give Harry a small percentage commission on our software sales every month. I think that this was probably a good idea. He could see that he was profiting from our delivery of new software.
While he worked for us he also taught college-level math classes in the evenings. At some point in the twenty-first century Harry quit in order to become a full-time teacher . He told Denise, who was his boss, that he was having trouble dealing with the pressure at TSI. The environment did not seem pressure-packed to me, but from my office — even with the door open — I could not hear any conversations.
I liked Harry a lot. For a time we were the only two males in the office, and it was very nice having someone with whom I could discuss a football game. Also, since we were almost exactly the same age, we had many of the same cultural landmarks.

Harry’s best friend was Vinny, his barber. Harry often told amusing stories about Vinnie or recited humorous quotes. I devoted a fair amount of effort to buying appropriate (and usually light-hearted) Christmas cards for the employees. One year I actually found one that featured a barber named Vinny.
Harry had a 24/7 tan. I assume that he went to a tanning studio. He did not seem like the kind of person who would do that, but you never know. One of my proudest achievements was to compare tans with him on my return from Hawaii. For the first and only time, my arm was darker than his.
Denise recruited and hired all of the new programmers who worked in our office in the twenty-first century. By this time we were using Monster.com for hiring. It was cheaper and better than newspaper ads, but it was still a time-consuming practice that tied up TSI’s most productive employee.
Brian Rollet was the first person that Denise hired. I remembered that he started while I was in Hawaii for the sales/vacation in December of 1975 (described here). I brought everyone back souvenirs for the employees. For Brian, whom I had never met yet, I purchased a hula-dancing bobble-head doll.
Brian was an Army vet. In fact, he was Airborne. Had I been doing the hiring, this would have given me pause in two different areas. 1) Why would anyone with a marketable skill like programming ability volunteer for three years in the Army? 2) Why would anyone jump out of a perfectly good airplane?
He also had a pretty long commute. He lived in Ware or Belchertown — one of those towns near the Mass Pike. There is no way to get to East Windsor from that area without driving through Springfield.
Denise was most upset about one of Brian’s most unprofessional traits — dozing off in the afternoon. She asked me what I would recommend. I told her that the obvious solution was caffeine. Who ever heard of a programmer anywhere who did not consume immense amounts of caffeine at work?
My second choice was to advise Brian to work something out with Harry, who was in the adjoining cubicle. If I were in Brian’s situation, I would have asked Harry to throw an eraser at me whenever he saw me nodding off. That would have worked, wouldn’t it?
When Denise called him on the carpet about it, Brian’s solution was to eat only salads at lunch. That might have helped a little, but Denise finally had to let him go. I don’t think that she was too satisfied with what he produced while he was awake anyway.
She confided to me that she would never again hire anyone who had been in the military.
Denise’s second hire, Michael Davis, worked out much better. He got up to speed very rapidly, and Denise really enjoyed working with him, and she definitely got to depend on him. Unfortunately, he did not stay at TSI very long. He moved to Pittsburgh, where he had family or a girlfriend or something.
The good news was that he liked the work at TSI well enough to work for us remotely for a period after he moved away. So, the transition was not too difficult. Of course, he could not answer the support line from Pittsburgh.
My most vivid memory of Michael was on our summer outing at (I think) Rocky Neck State Park. He took me out on his small sailboat. People from Kansas do not often get opportunities like this. Of course, he did all the sailing. My only job was to duck my head down by my knees when he decided to swing the sail around.
I remember that after Michael had been at TSI for a year or so he decided to buy a new car. Well, not a NEW car, but a NEWER car. He chose a Volkswagen; I don’t remember the model. The few times that I shopped for a car I never considered buying a used one. I would be too afraid that I was just buying someone else’s problems. Nevertheless, Michael seemed satisfied with his purchase.
I don’t remember much about Sean Finnegan7. In fact, I had to ask Denise about him. He worked for TSI for two months in 2010. He was apparently a pretty good programmer, but he had difficulty talking with clients on support calls.
Jason Dean8 lived in the Springfield area. Before coming to TSI he had worked in Friendly’s IT department. He joined us in October 2007 and was still employed when we closed down the company in 2014.
Denise got along with Jason nearly as well as she did with Michael. She was very satisfied with his attitude and performance.
I did not really get to know Jason too well until Denise started working remotely in 2013. One thing that I quickly learned was that he was a terrific bowler. He had bowled at least three 300 games, which blew my mind. He had quite a few bowling balls. He told me that getting the ball to spin correctly depended on both the surface of the ball and the surface of the lane. So, different balls were needed depending on the condition of the lanes..
I was very surprised to learn that Jason’s bowling balls had only two holes. He did not have a hole for his thumb.
Jason knew my bridge friends Bob and Shirley Derrah from bowling in Springfield.
Jason and his wife were, in my opinion, fanatical about coupons, Groupons, and all other ways of obtaining discounts. They were always shopping for bargains. They switched their cell service from Verizon to T-Mobile to save on phone charges. However, the T-Mobile phones got no signal in their apartment. They got their money back, but it was a big hassle.
Jason had a son when he started working at TSI. His second son was born quite prematurely, and it was touch-and-go for a while, but he pulled through and was quite healthy the last that I knew. The family also had three rescue cats who were too eccentric for my tastes.
In his middle school in Springfield Jason had twice been a spelling champion. He was the only other person whom I have ever met who competed in the national spelling bee.
Jason and his family loved Disney World. They spent every vacation there, and they always stayed in the same Disney hotel. They monitored the situation very closely and always made reservations on the first day that the discounted fares were offered.
Jason had an older brother who lived at home with his parents. He spent most of his time in the basement playing Worlds of Warcraft. Although he had never worked, Jason insisted that he was a brilliant guy. He urged Denise to consider hiring him. I don’t remember the details, but he never came to the office. I am not sure that he could drive.
Jason actually contacted the Dr. Phil show to try to get them do do an intervention to help his brother get out of his shell. His parents vetoed the idea.
Jason and his parents were very conservative. He could not believe that Obama had defeated Romney in 2012. He told me that he suspected that there had been voting fraud, but he readily admitted that he had no evidence.
1. By the time that we moved the office to East Windsor, CT, in 1999 TSI had eight phone lines.
2. In 2021 Harry Burt is teaching math at Naugatuck Community College. His LinkedIn page is here.
3. Casual Corner closed all of its stores in 2005. Since then the headquarter building in Enfieldhas been used by Brooks Brothers, which also is now in bankruptcy.
4. Riverside Park was acquired by Premier Parks in 1996, a couple of years after Steve started at TSI. The name was changed to Six Flags New England.
5. Steve Shaw sent me emails a couple of times. In the one in February of 2000 he reported that he was working at the Phoenix, and they had sent him to classes on Websphere and Java. However, we never got together. Because he has such a common name, It was difficult to locate him, but I finally found his LinkedIn page. You can see it here.
6. I think that Brian Rollet lives in the Ware, MA, area in 2021.
7. Sean Finnegan’s LinkeIn page is here.
8. Since TSI closed in 2014 Jason Dean has worked at ESPN as Application Support Analyst III. His LinkedIn page is here.